A building automation system or BAS is a network of controlling and monitoring devices mainly responsible for the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) control system in large facilities and commercial buildings.
Building automation systems are most commonly implemented in large facilities such as healthcare facilities, schools, universities, hotels, residential buildings, and data centers. A BAS network allows building operators to supervise and control the HVAC systems from a centralized location known as the Building Management System or BMS.
Main BAS Components
A building automation system is mainly composed of hardware devices such as routers, switches, supervisory controllers, application, and system DDC controllers, as well as sensors, actuators, relays, and drives.
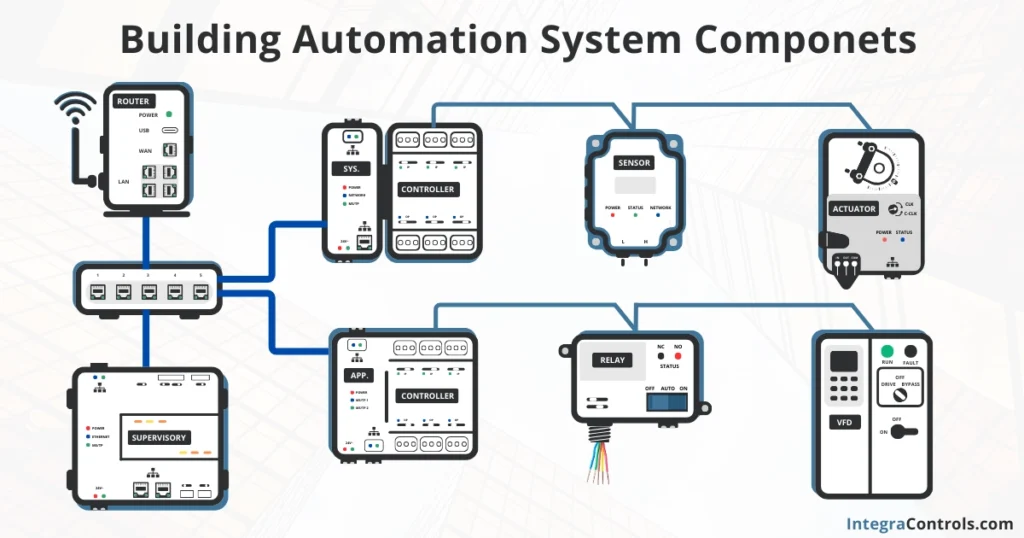
These devices interconnect and communicate through communication protocols such as BACnet® or Modbus®, creating a network of controlling and monitoring devices that are known as the BAS.
Why do we need a BAS?
A building automation network is required due to the system approach that large commercial HVAC systems exhibit in their operations. In other words, large HVAC systems cannot efficiently operate without communication among their components.
To illustrate this concept, we will use a variable air volume system as an example. In a VAV system, the air handling unit (AHU) and the VAV boxes are physically separated from each other, and each one has its own controller, also distanced from one another.
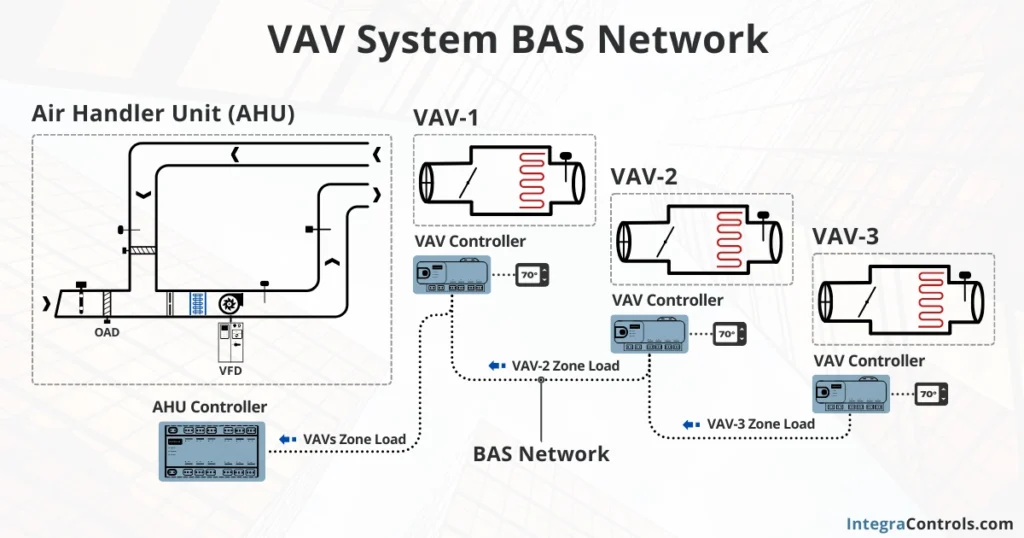
However, for a VAV system to operate effectively, the VAV Boxes and the AHU have to talk to each other; in other words, they need to share information to properly adjust their setpoints based on zone heating or cooling demand.
Therefore, to enable communication among these devices, a network is necessary; this network is known as the building automation system. The BAS allows data such as occupancy schedules, load demand, and equipment faults to be shared among all the devices in the network, improving overall system performance and efficiency.
BAS Capabilities
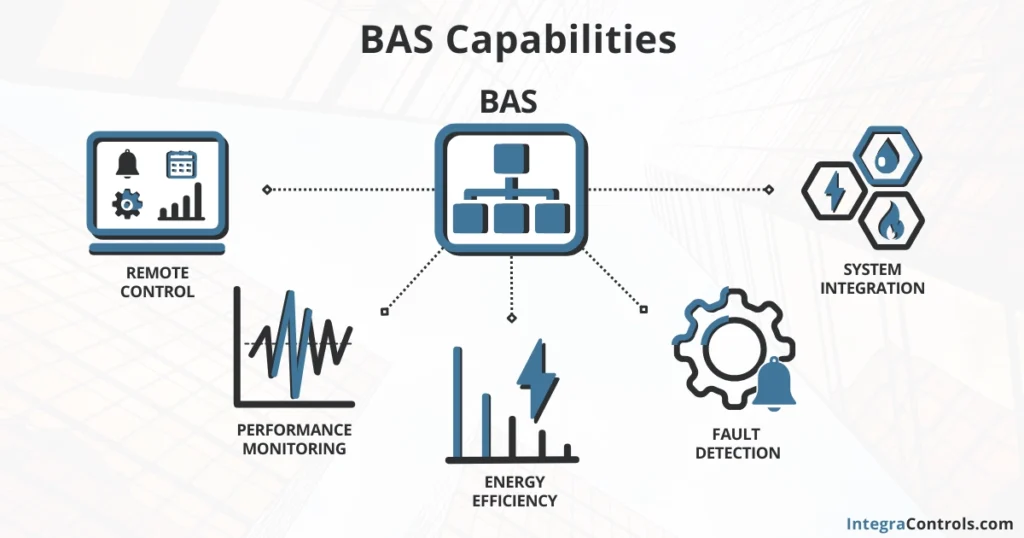
Having a Building Automation System enables capabilities such as:
- Remote Control: Building operators can remotely access and control all the systems and equipment inside the BAS.
- Equipment Performance Monitoring: Historic data trends allow building operators to observe equipment performance and detect any anomalies in their operation.
- Energy Efficiency: A building automation network unlocks the possibility of reducing power consumption through system control optimization and allows energy monitoring through an energy management system interface.
- Fault Detection: Fault detection algorithms notify building operators of equipment and component failures, reducing response time to failures and preventing possible business operation interruptions.
- System Integration: A BAS network allows integration with other building systems such as emergency power, domestic water, and fire alarm, providing additional visibility and control over the building assets.
BAS and BMS
Lastly, it’s worth mentioning that a BAS by itself has its limitations. As we mentioned, a BAS is simply a network of devices. In order for operators to view and control these devices, they need to use a front-end interface known as the Building Management System or BMS.
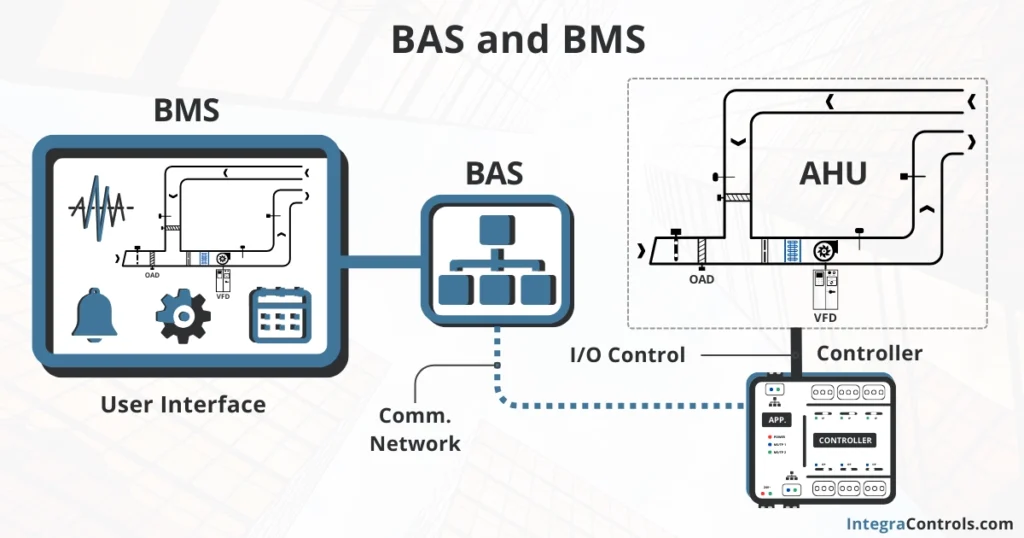
It’s within the Building Management System where operators can supervise and control the different devices that are part of the Building Automation Network.
Although the terms BAS and BMS are commonly used interchangeably in the HVAC and Building Automation industries, they are not the same thing. In this article; BAS vs. BMS: What’s the Difference?, we go over the main differences between these two systems and where the confusion comes from.
In Summary
A building automation system is a network of hardware devices that constitute the backbone of the smart building infrastructure in large facilities and commercial buildings, unlocking supervision and control capabilities over the building assets and ultimately contributing to overall business operation.



